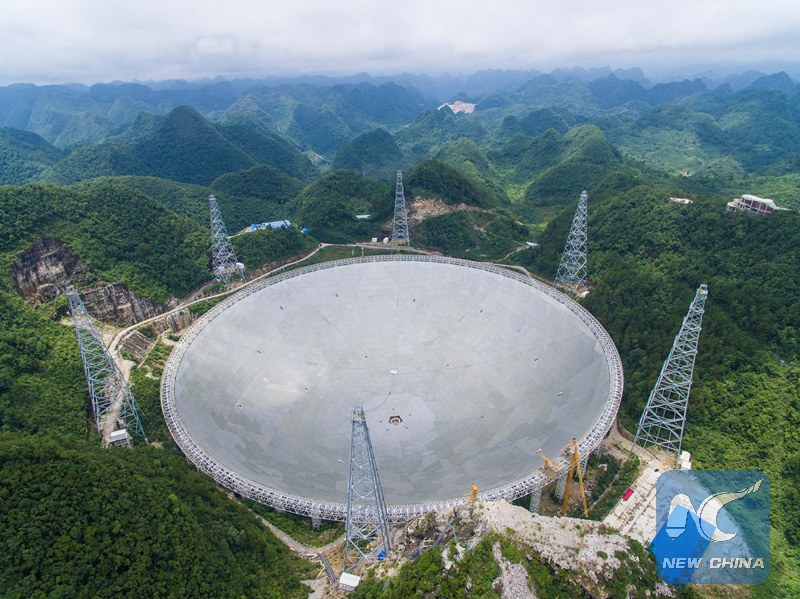

The aerial photo taken on July 3, 2016 shows the FAST in Pingtang County, southwest China's Guizhou Province. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
GUIYANG, July 3 (Xinhua) -- Installation was completed on the world's largest radio telescope on Sunday morning as the last of 4,450 panels was fitted into the center of the big dish.
Hoisting of the last triangular panel to the reflector, which is the size of 30 football fields, began at 10:47 a.m. and lasted about an hour. It was a landmark step for the telescope's planned launch of operations in September.
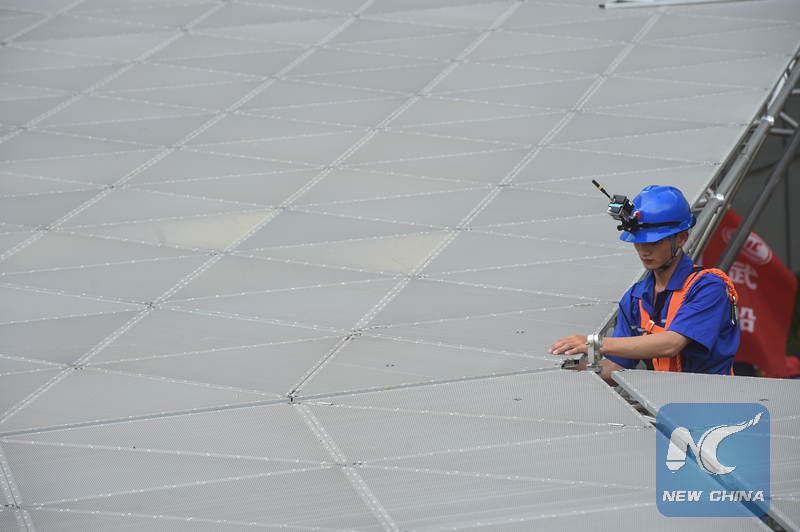

A worker installs the last triangular panel to the reflector of the FAST on July 3, 2016. (Xinhua photo/Ou Dongqu)
About 300 people, including builders, experts, science fiction enthusiasts and reporters, witnessed the installation at a karst valley in Pingtang County in the southwestern province of Guizhou.
"The telescope is of great significance for humans to explore the universe and extraterrestrial civilizations," said Liu Cixin, a renowned science fiction writer, at the site.
"I hope scientists can make epoch-making discoveries," said Liu, who won the 2015 Hugo Award for Best Novel.
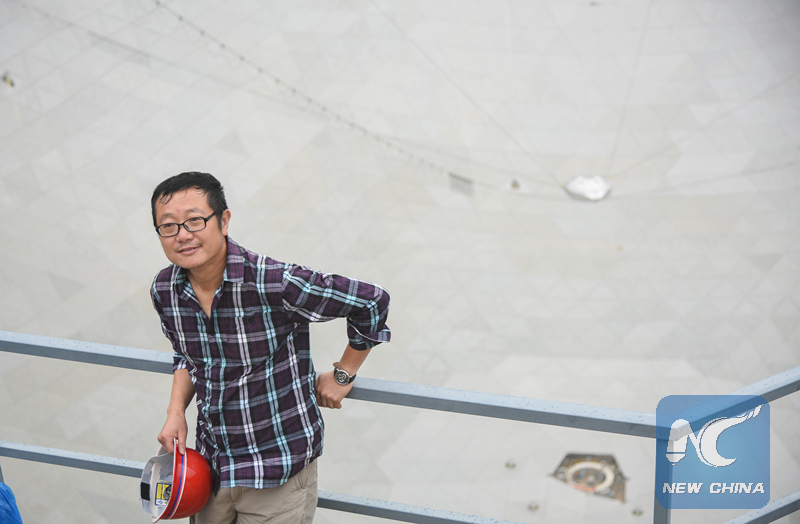

Chinese prominent science fiction writer Liu Cixin is seen at the site to witness the installation completion on the FAST. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
Scientists will then begin debugging and trial observation of the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), said Zheng Xiaonian, deputy head of the National Astronomical Observation (NAO) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which built the telescope.
The project has the potential to search for more strange objects to better understand the origin of the universe and boost the global hunt for extraterrestrial life, said Zheng.
Zheng said the radio telescope will be the global leader for the next 10 to 20 years.
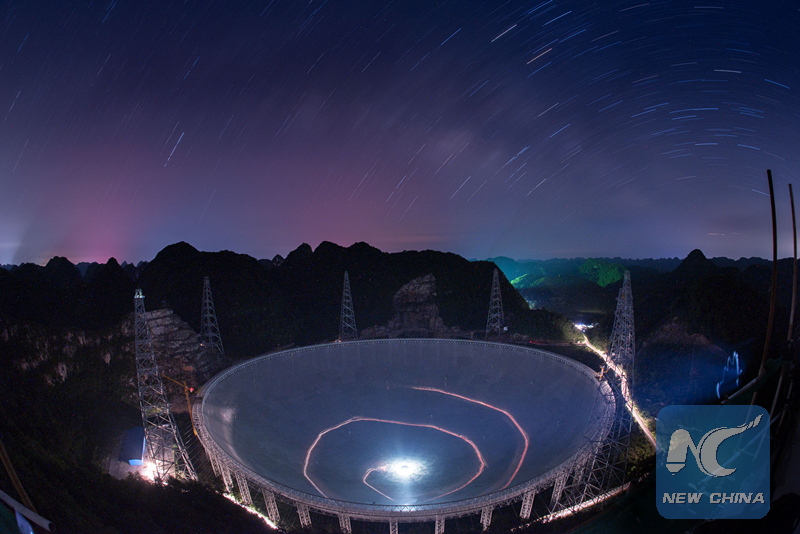

Photo taken on June 27, 2016 shows the FAST at night. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
In the first two or three years after its completion, the telescope will undergo further adjustment, and during that period Chinese scientists will use it for early-stage research. After that, it will be open to scientists worldwide, said Peng Bo, director of the NAO Radio Astronomy Technology Laboratory.
Scientists can also carry out remote control and observation in other cities such as Beijing, more than 2,000 kilometers from the telescope site, said Peng.
Upon completion, the telescope will dwarf Puerto Rico's Arecibo Observatory, which is 300 meters in diameter. It will also be 10 times more sensitive than the steerable 100-meter telescope near Bonn, Germany, he said.
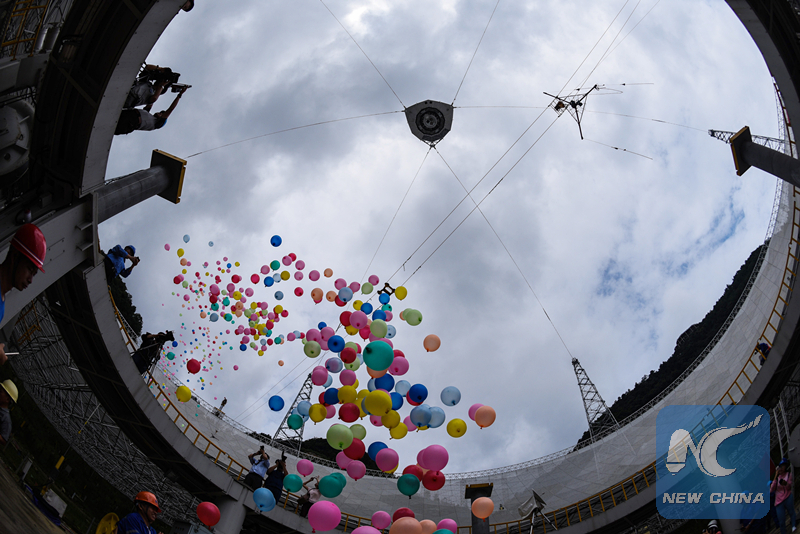
Balloons are released to celebrate the complete installation on the FAST. (Xinhua photo/Ou Dongqu)
"Most of the technology and materials are domestically made," said Wang Qiming, chief technologist of the FAST project.
Among the 7 FAST receivers, five were domestically made and another two were co-produced by Chinese, Australian and American institutions.
Work on the 1.2-billion-yuan (180 million U.S. dollars) FAST project began in 2011.
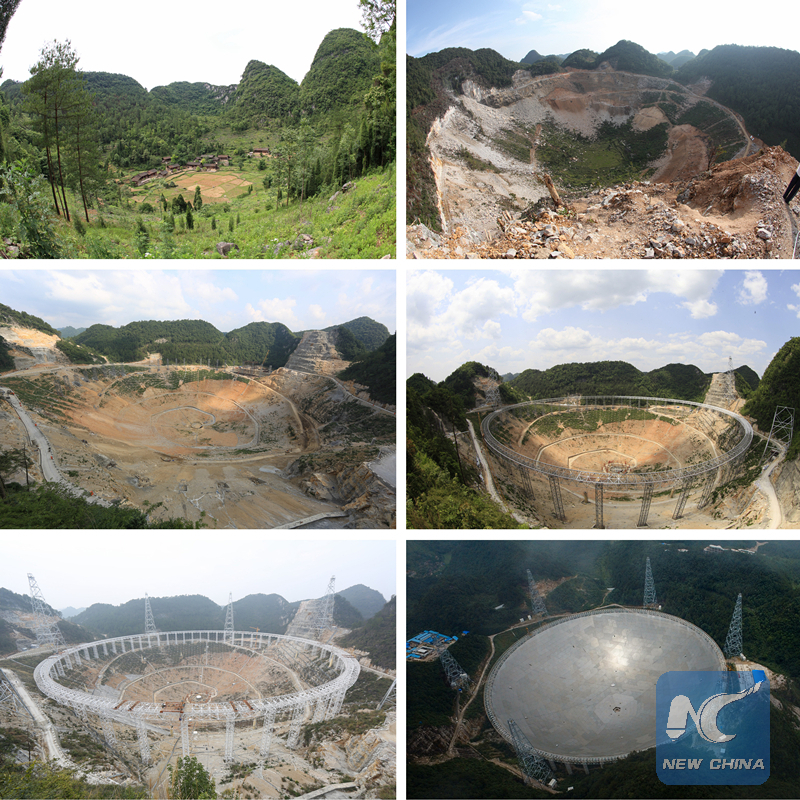

The combo picture show the construction process of the FAST. (Xinhua photo)
EYE ON THE SKY
Radio telescopes have made major astronomical discoveries, such as pulsars, quasars and cosmic microwave background radiation. Among the 10 Nobel Prizes in physics awarded for discoveries related to cosmology and space, six were attributed to radio telescopes.
"As the world's largest single aperture telescope located at an extremely radio-quiet site, its scientific impact on astronomy will be extraordinary, and it will certainly revolutionize other areas of the natural sciences," said Nan Rendong, chief scientist with the FAST Project.
FAST will enable astronomers to get a jump-start on many scientific goals, including surveying neutral hydrogen in distant galaxies and detecting faint pulsars.
Scientists also expect breakthroughs on pulsars, the highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars that emit a beam of electromagnetic radiation. So far more than 2,000 pulsars have been detected.
"Pulsars can help scientists study gravitational waves," Chen added.
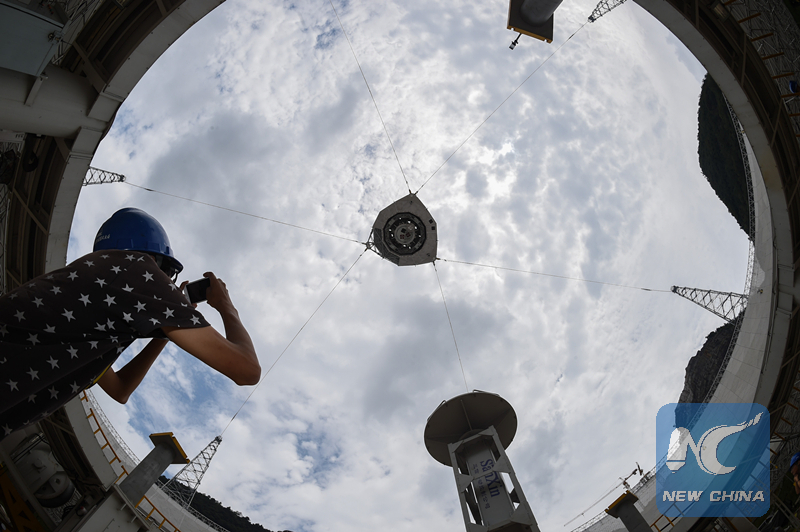

A working staff takes photos of a cabin of the FAST above the dish-like reflector on June 29, 2016. (Xinhua photo/Ou Dongqu)
As China joins international efforts in gravitational wave detection, FAST will help improve the chances of detecting low frequency gravitational waves, said Wu Xiangping, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, who predicted great breakthroughs in this area in the years ahead.
For ordinary people, perhaps the most exciting goal of FAST is the search for alien life.
In two or three years, scientists could find amino acids, the foundation block of life. There is a great chance that people will someday find life on other planets or galaxies, said Li Di, an NAO researcher.
"FAST's potential to discover an alien civilization will be 5 to 10 times that of current equipment, as it can see farther and darker planets," said Peng Bo.
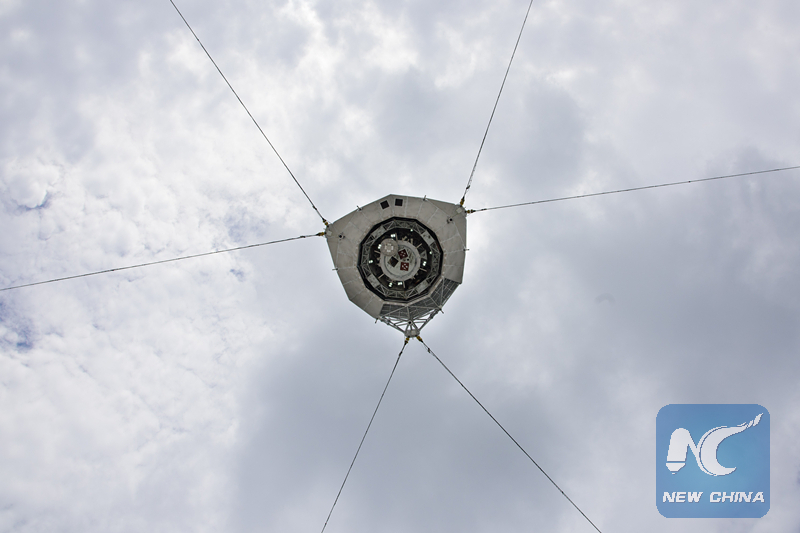

Photo taken on June 29, 2016 shows a cabin of the FAST above the dish-like reflector. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
"THANK THE ALIENS"
It has been more than two decades since Chinese scientists proposed building FAST in Guizhou.
In 1994, site surveying started on geo-morphological features and the distribution of karst depressions, climate, engineering environment, social environment, and radio interference.
Engineer Zhu Boqin worked on the site selection 20 years ago. He recalled that after more than two hours trudging on the rugged mountain road, about 150 kilometers south of the provincial capital Guiyang, he was impressed by the sight of a large, round depression embraced by verdant hills.
It was home to 65 people from 12 families in a closed-off world called "Green Water Village." Lacking electricity, the villagers had a clear view of the starlit sky at night.
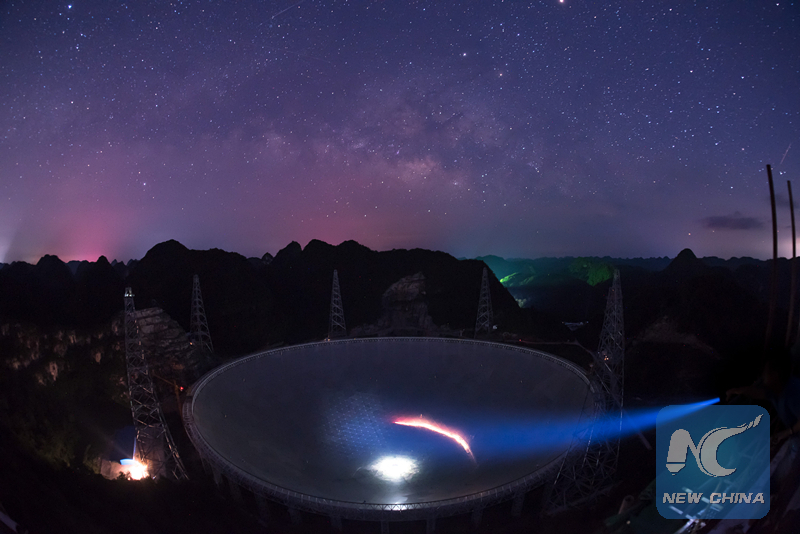

Photo taken on June 27, 2016 shows the FAST at night. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
Zhu said that though the villagers did not understand the radio telescope, they were excited when scientists explained that they would use it to search for intelligent beings on other planets.
Formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum, the karst formations create naturally spherical depressions. This saved efforts in digging hollows for the dish, said Li Di.
The three hills around the depression formed an equilateral triangle, creating a perfect holder for the dish, Li said.
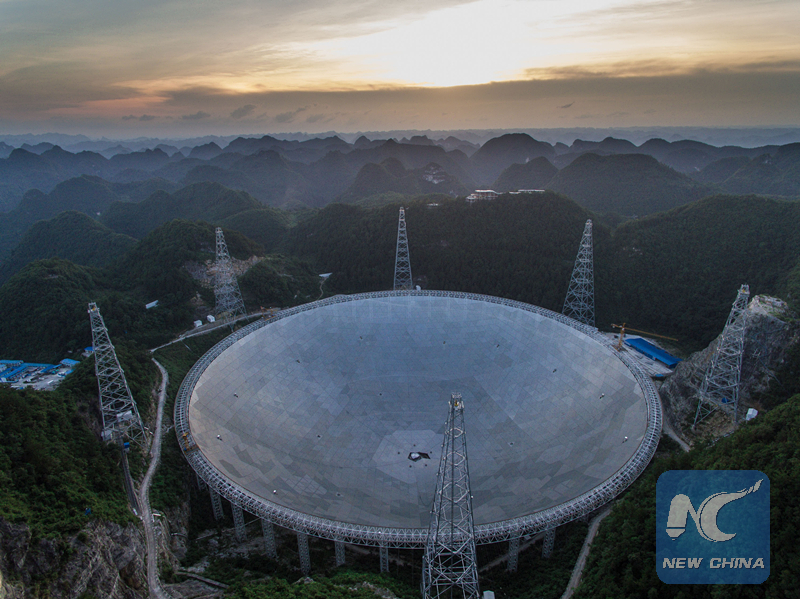

Photo taken on June 27, 2016 shows the FAST at sunset. (Xinhua photo/Liu Xu)
The karst formation is also good for draining rainwater and protecting the reflector, Zhu said. Moreover, the surrounding area has "radio silence" as there are no towns within a 5-km radius, and only one county seat within 25 km.
The site was eventually chosen for the FAST Project.
Residents were moved away to towns in 2009, where they enjoy better living standards. Villagers in nearby communities admired their luck, saying they should "thank the aliens."
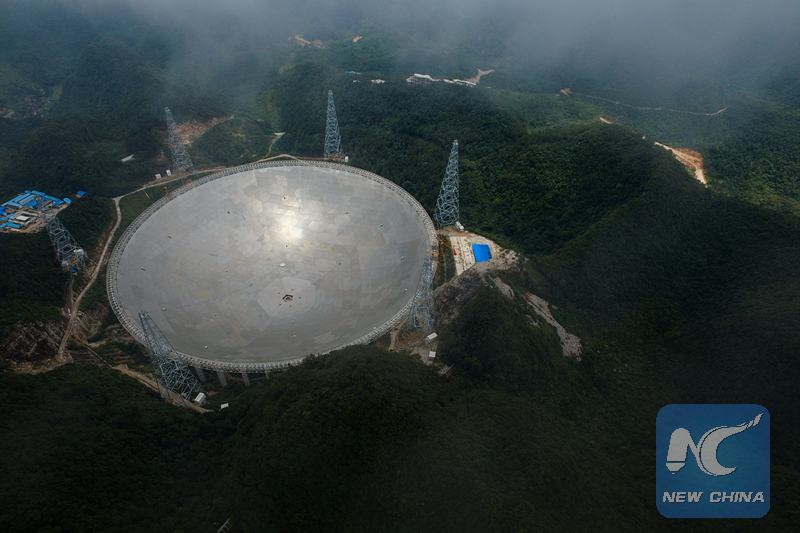

The photo taken on July 3, 2016 shows the FAST. (Xinhua photo/Ou Dongqu)
"I never thought the first time I would move would be to make way for a telescope," said Yang Chaolan, 62, who now lives in a government-funded two-story building in the seat of Kedu Township.
Her son, Yang Tianyou, 29, plans to open a restaurant or supermarket in hopes that growing tourism will bring him fortune.
According to a government plan, 9,110 residents living within five kilometers of the telescope will be resettled in Pingtang County and Luodian County in four settlements by the end of September.

