
X-ray fluorescence instrument set up for the scan of La Miséreuse accroupie, with Emeline Pouyet of Northwestern University (left) and Sandra Webster-Cook of the Art Gallery of Ontario. © Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO)
AUSTIN, TEXAS, Feb. 17 (Xinhua) -- An international team of scientists has used multiple modes of light to uncover details hidden beneath the visible surface of Spanish painter Pablo Picasso's masterpiece "La Misereuse accroupie" or "The Crouching Woman."
Researchers released their findings on Saturday's press conference at the ongoing four-day annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science held in Austin, Texas.
The 1902 oil painting, owned by Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO) in Canada, depicts a crouching and cloaked woman, painted in white, blues, grays and greens.

Pablo Picasso. La Miséreuse accroupie, 1902. Oil on canvas, 101.3 x 66 cm (39 7/8 x 26 in.). Art Gallery of Ontario. Anonymous gift, 1963. © Picasso Estate.
Researchers used non-invasive portable imaging techniques, including infrared reflectance hyperspectral imaging and then an X-ray fluorescence imaging instrument to detail those buried images.
It shows that Picasso painted over another painter's work after rotating it 90 degrees to the right, using some of the landscape forms in his own final composition. For example, Picasso incorporated the lines of the cliff edges into the woman's back.
Picasso also made a major compositional change, the study showed. The artist initially painted the woman with a right arm and hand holding a disk but then covered them with her cloak in the final work.
Marc Walton, a research professor of materials science and engineering at Northwestern University said, "Picasso had no qualms about changing things during the painting process."
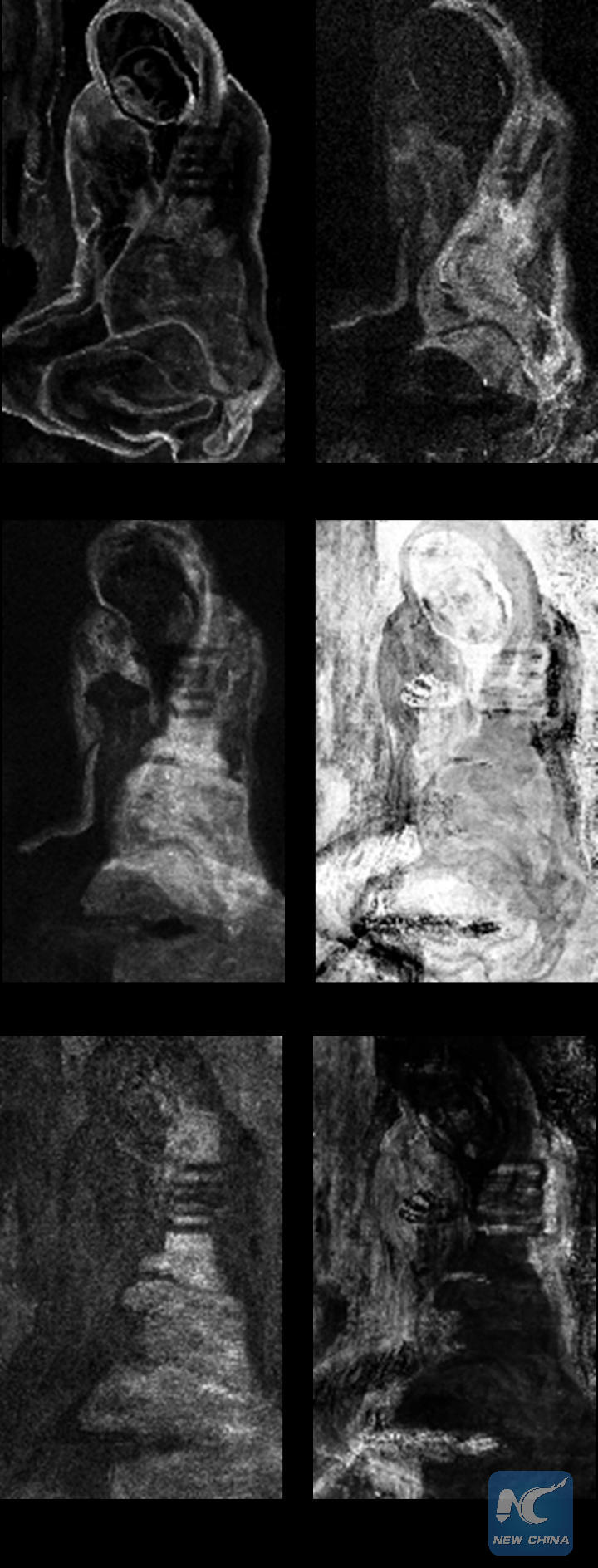
Distribution maps of a few elements characteristic of the pigments present in the different paint layers of La Miséreuse accroupie. © Northwestern University/Art Institute of Chicago Center for Scientific Studies in the Arts (NU-ACCESS)
The imaging techniques allowed art collectors to better understand Picasso's style, influences and process.
"When we saw the rendering of the lead elemental map, it became clear to me that the arm hidden under the visible surface of 'La Misereuse accroupie' is the same as the proper right arm of a crouching woman in a Picasso watercolor recently sold at auction," said Kenneth Brummel, the AGO's assistant curator of modern art. The watercolor is titled "Femme assise" (1902).
"We now are able to develop a chronology within the painting structure to tell a story about the artist's developing style and possible influences," said Sandra Webster-Cook, AGO's senior conservator of paintings.

